 Develop
Develop
Build your own marine virtual lab making use of a range of available web services that access and process data.
What are web services?
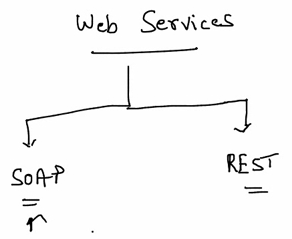 |
Within the envisaged e-infrastructure of LifeWatch, data exchange and data analysis are largely based on the use of web services. Web services are systems that allow communication between two computers over the web, and allow the user to access the most recent and up-to-date information directly from within other applications. Web services can roughly be divided into two categories: SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) and REST (Representational State Transfer). SOAP has the ability to discover and describe web services via the WSDL (Web Services Description Language) standard, but usually needs a platform dependent library to work. REST uses standard HTTP (and JSON) and is much simpler to use, but lacks a standard way of description (as is the case with SOAP WSDL). |
Where to find the web services?
|
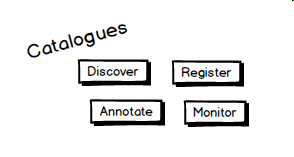
Several catalogues exist listing the available web services. The BiodiversityCatalogue (developed by BioVeL) is a curated catalogue of available web services that are specific to the interests of the biodiversity science community. This catalogue is related to the BioCatalogue, which focus is on life science web services. Both catalogues are community-oriented websites where service providers and community experts can register and curate services, and where users can discover them. Users can browse the catalogues and access full search options for services, checking their status and availability. Geographic web services in general are listed in numerous spatial data catalogues, often with a specific contextual scope. Spatial data catalogue systems like the GeoNetwork Opensource offers catalogue applications for managing spatially referenced resources and documenting their web service parameters. Specifications of the geographic web services are specified by the OGC standards. |
 |
How to access the web services?
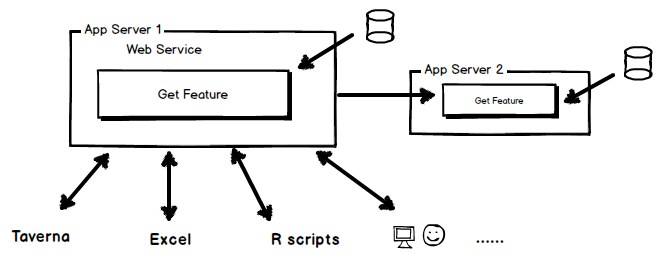 |
Web services can be accessed from within several platforms or software. Web services can for example be built into PHP web pages, service management tool, R scripts, and even spreadsheets software like MS Excel. Secondary application servers can use the web service to access data from the provider and combine this output with other local processes. Some example implementations (specific for the WoRMS web services) can be found here. |
How to connect web services into workflows?
|
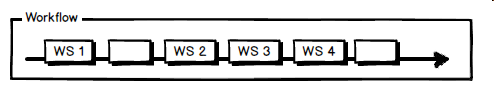
Web services can be executed consecutively, constituting so-called workflows, for all kind of analytical purposes. The existing BioVeL workflows can be downloaded from myExperiment and can be run in the Taverna Workbench. The latter also enables you to edit workflows and to create your own workflows. |
 |
